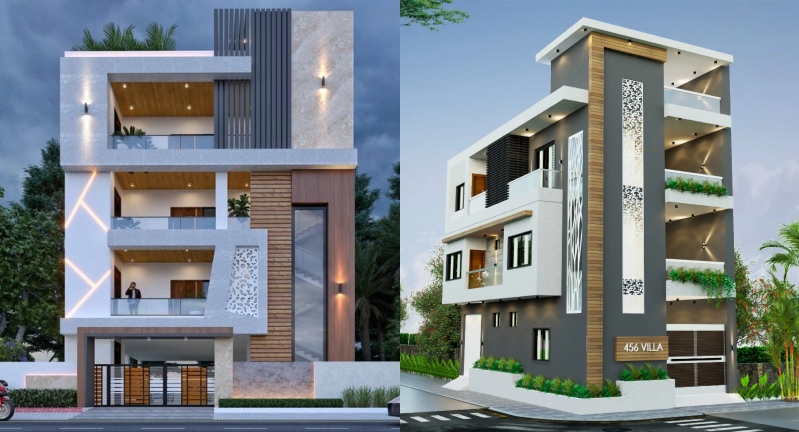
House elevation is a crucial part of architectural design and construction, outlining visual appeal, structural integrity, and then building functionality. In core, it is known to be the vertical measurement of a house relative to its surrounding place or base level. Further than aesthetic significance, house elevation act as a crucial role in securing natural disasters like floods, high energy efficiency and enhancing space utilization.
In this complete guide, we will move into the known about house elevation, types, their benefit, and so more.
Table of Contents
What is House Elevation?
House elevation includes the vertical positioning and architectural design of the structure, defining its height, proportions, and then overall appearance. Also, it encompasses improving the building base over ground level, often through the use of the foundation system, retaining wall or stilts. The elevation is influenced by various factors such as climate conditions, topography, building codecs, aesthetic needs, and so more.
Types of House Elevation
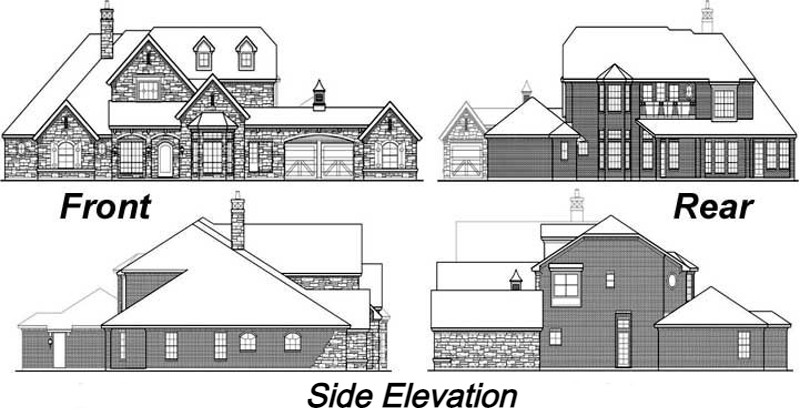
House elevation act as a crucial role in defining the aesthetic appeal and functionality of a residential structure. Different kinds of house elevation designs are available to various architectural styles, site conditions, and the needs of homeowners. Let’s explore the four basic types of house elevation;
1. Front Elevation
The front elevation designs are also known as a faced or frontal view. It is the most crucial and visually impact element of a house. It showcases the features of architectural and exterior completeness that define the structural character and presence. It frequently incorporates elements like doors, windows, balconies, decorative items, and so more to develop a welcoming and pleasing façade. Homeowners may personalize their front elevation to match their needs, in case it is traditional, modern, or else, while adhering to local building codes and aesthetics.
2. Rear Elevation
Compared with the front elevation, the rear elevation of a house is frequently less ornate and decorative things. But, it is equally crucial when it comes to spatial organization and functionalities. It includes elements like back doors, patios, decks, and outdoor living areas that link the interior living areas with the backyard. It may prioritize security, outdoor entertaining, or else increasing the natural light and views that depend upon the site orientation and tertian considerations. Design in the rear elevation improves overall livability and usage of outdoor spaces when maintaining peace with the architectural style of the residence.
3. Side Elevation
It offers a profile view of the house from the left or right side, enlightening the structural massing, fenestration design, roofline and more. They are highly needed for understanding the spatial relationship over local properties, setback needs, and chances for day lighting and ventilation. Regards on site constraints and the objective of design, this elevation may feature architectural aspects like dormers, gables, and design objectives to develop visual interest and architecture along the structural perimeter.
4. Cross-Sectional Elevation
Cross-sectional elevation drawings depict a vertical slice over the house, showing the internal design, floor levels, height of ceilings, and building components from side to side and front to back. They offer valuable insight into the spatial organization, vertical connectivity within the house, circulation flow, and guiding the design of steps and multi-level spaces. They also facilitate coordination phases make ensure compliance with building codes and structural integrity.
Things to Consider While Choosing The House Elevation for Your New Home

Site Investigation
Before going to house elevation, an entire site is needed to assess soil conditions, drainage ways, risk of flood, and then regulatory requirements. This assessment reports the chance of correct elevation plans and basis system customized to the site unique features.
Environmental impact
Home elevation can impact the surrounding environs through changes in drainage path, soil deterioration, and natural disturbance. So, implements suitable design that consist porous paving, rainwater harvesting and neighborhood landscaping, alleviates environmental impacts and then entire ecological stability.
Structural balance
It contains structural improvements in order to support the high vertical load and meet outer force which includes wind, seismic movements, soil conditioning and so more. Including skilled architects is needed to assessing the structure of existing floor and then makes certain adherence to structural principles.
Construction Codes and Policies
Adherence to regional construction codes, zoning regulations, and regulatory guidance is important whilst creating plans for home elevation tasks. Those policies dictate proper construction sizes, setback provisions, flood region types, and structural design criteria to ensure security, stability, and environmental sustainability.
Benefits of House Elevation
Stronger Resilience
House elevation complements the strength of residential structures in opposition to natural screw-ups, including storms, tsunamis, and seaside erosion. Elevating homes on stilts or supported foundations enhances structural harmony, decreases exposure to wind and water injury, and ensures continuity of occupancy throughout crises.
Extended residing space
By advancing the base of the house, owners can capitalize on previously underutilized spaces, which include basements and garages, or move slowly spreads. This creates extra living areas for bedrooms, home workplaces, leisure spaces, or storage, thereby improving the functionality and price of the property.
Improved ventilation
Stilted or raised foundations promote natural airflow, airflow, and thermal comfort within the house, decreasing reliance on mechanical heating and cooling structures. Elevating homes also decreases contact with damp or moist soil, mitigating moisture infiltration, mold growth, and humidity-related issues.
Flood Mitigation
Elevating houses beyond flood-susceptible areas protects opposition to water harm, lowers flood range speeds, and keeps asset expenses. Stilted or raised floors present home areas beyond the bottom flood elevation, underestimating the hazard of inundation for the duration of heavy rainfall or storm surges.
Aesthetic enchantment
The double floor home elevation design gives possibilities for innovative architectural expression, letting house owners customize the exterior façade, entranceway, and landscaping to reflect their style and selections. Elevating houses command interest, provide commanding perspectives, and contribute to the visual range of the constructed environment.
Bottom Line
House elevation is a multifaceted architectural function that mixes capability, aesthetics, and resilience to beautify the livability, safety, and sustainability of residential systems. Whether addressing flood danger, optimizing area utilization, or embracing revolutionary design solutions, house elevation offers tangible benefits for house owners, locals, and the surroundings alike. By appreciating the various kinds, concerns, and benefits of house elevation, stakeholders can make knowledgeable decisions to create resilient, adaptable, and aesthetically attractive homes for generations to come.

